Family-owned since 1985
We provide you one-stop manufacturing services including 3D printing, tooling, moulding, die casting and secondary processes.
TS6949:2016 & ISO 9001:2008 Certified
IML/IME
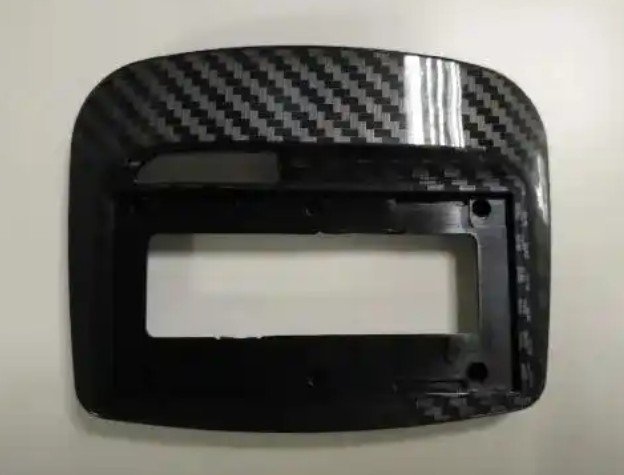
In-Mold Labeling (IML) is an advanced labeling technique used in plastic injection molding, where a pre-printed label is placed inside the mold before injecting molten plastic. The label fuses with the plastic, creating a durable, high-quality, and seamless design.
This method is widely used in food packaging, consumer goods, medical devices, and industrial components and a lot more.
IML in plastic injection molding eliminates the need for secondary labeling processes, making it an efficient and environmentally friendly alternative to traditional labeling techniques.
The challenges are higher setup costs, complex label placement and material compatibility. However at Layne Tech, we have over 20+ years’ experience in IML process. Let’s discuss how our IML expertise can add value to your products and streamline your manufacturing process.
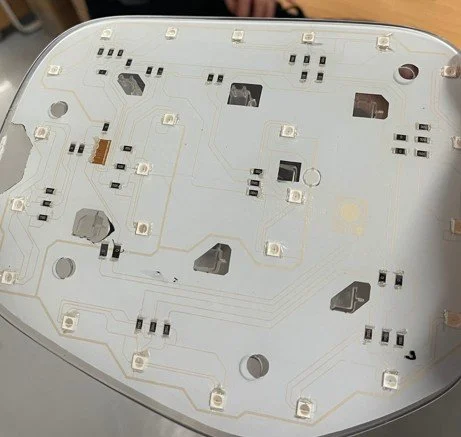
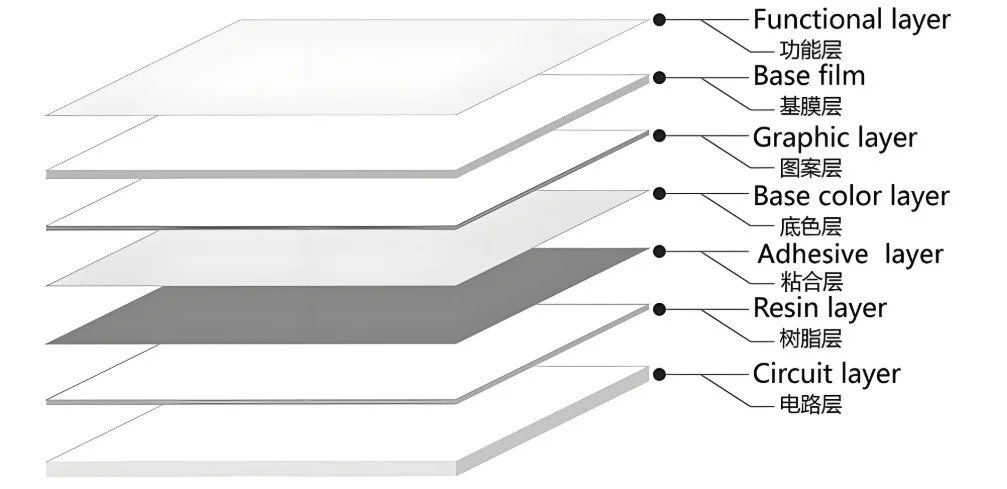
In-Mold Electronics (IME) is a cutting-edge technology in the injection molding industry that integrates electronic circuitry directly into molded plastic components. By embedding conductive inks, sensors, and other electronic elements within the structure of an injection-molded part, IME enables the production of lightweight, compact, and highly functional electronic devices. This innovation is revolutionizing industries such as automotive, consumer electronics, medical devices, and smart packaging.
The IME Process
1. Printing the Electronic Circuit
The process begins with screen printing conductive inks (usually silver or carbon-based) onto a flexible polymer film. These inks form the electrical circuitry, which can include resistors, capacitors, antennas, and even sensors.
2. Adding Functional Components
After printing, additional electronic components such as LEDs, sensors, and touch interfaces can be mounted on the film. These components are designed to withstand the subsequent molding process.
3. Forming the 3D Structure
The printed and assembled film undergoes thermoforming, a process that shapes it into a three-dimensional form without damaging the printed electronics.
4. Insert Molding
The formed structure is then placed into an injection mold, where plastic resin is injected to encapsulate the electronic components. The materials used are typically polycarbonate (PC), polyamide (PA), or acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS), ensuring durability and high mechanical strength.
5. Final Assembly and Testing
Once molded, the part undergoes electrical testing and quality inspection to ensure functionality. Additional finishing processes, such as laser etching or protective coatings, may be applied to enhance durability and aesthetics.
Key Advantages of IME
• Lightweight and Compact Design: Eliminates the need for bulky circuit boards, reducing size and weight.
• Increased Durability: The embedded electronics are protected from moisture, dust, and mechanical stress, enhancing product lifespan.
• Simplified Manufacturing: Reduces assembly steps and costs by integrating electronics directly into molded parts.
• Enhanced Aesthetic and Functional Design: Enables seamless touch interfaces, backlighting, and interactive features without compromising appearance.
• Sustainability: IME can reduce electronic waste by eliminating traditional PCBs and excess wiring.
Applications of IME in Different Industries
1. Automotive Industry
• Touch-sensitive dashboards and controls
• Backlit switches and capacitive buttons
• Integrated lighting for interior aesthetics
• Smart surfaces with haptic feedback
2. Consumer Electronics
• Smartphone and tablet interfaces
• Wearable technology (smartwatches, fitness trackers)
• Flexible and foldable displays
• Embedded NFC and RFID technology
3. Medical Devices
• Wearable biosensors for health monitoring
• Flexible medical patches with integrated electronics
• Antimicrobial surfaces with embedded sensors
4. Smart Packaging and IoT
• Interactive packaging with touch controls
• Temperature and freshness sensors for perishable goods
• Embedded NFC for product authentication
5. Aerospace and Defense
• Lightweight control panels for aircraft and military vehicles
• Flexible sensor arrays for structural health monitoring
• Integrated antenna systems for secure communication
Future of In-Mold Electronics
The growing demand for smart, lightweight, and durable electronic products is driving the adoption of IME technology. Innovations in conductive ink materials, flexible substrates, and integration with 5G and IoT will further expand its applications. As manufacturers seek cost-effective and sustainable solutions, IME is set to become a key enabler of next-generation electronic design.
Conclusion
In-Mold Electronics (IME) represents a major leap forward in injection molding, offering unparalleled integration of electronics into plastic components. With its ability to enhance product functionality, durability, and aesthetics, IME is rapidly transforming industries ranging from automotive to healthcare. As technology advances, we can expect even more innovative applications that redefine the possibilities of smart, embedded electronics.